
#Aufbau principle full
Similarly, the full subshell boosts the atom’s stability. The half-filled subshell increases orbital stability by exhibiting electron repulsion.
There are numerous outliers, such as chromium’s electron configuration. Carbon, for example, has 6 electrons and its electrical configuration is 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 2. The Aufbau principle could be used to explain the placement of electrons in an atom and the energy levels associated with them. The primary quantum number is denoted by ‘n,’ and the azimuthal quantum number is denoted by ‘l.’
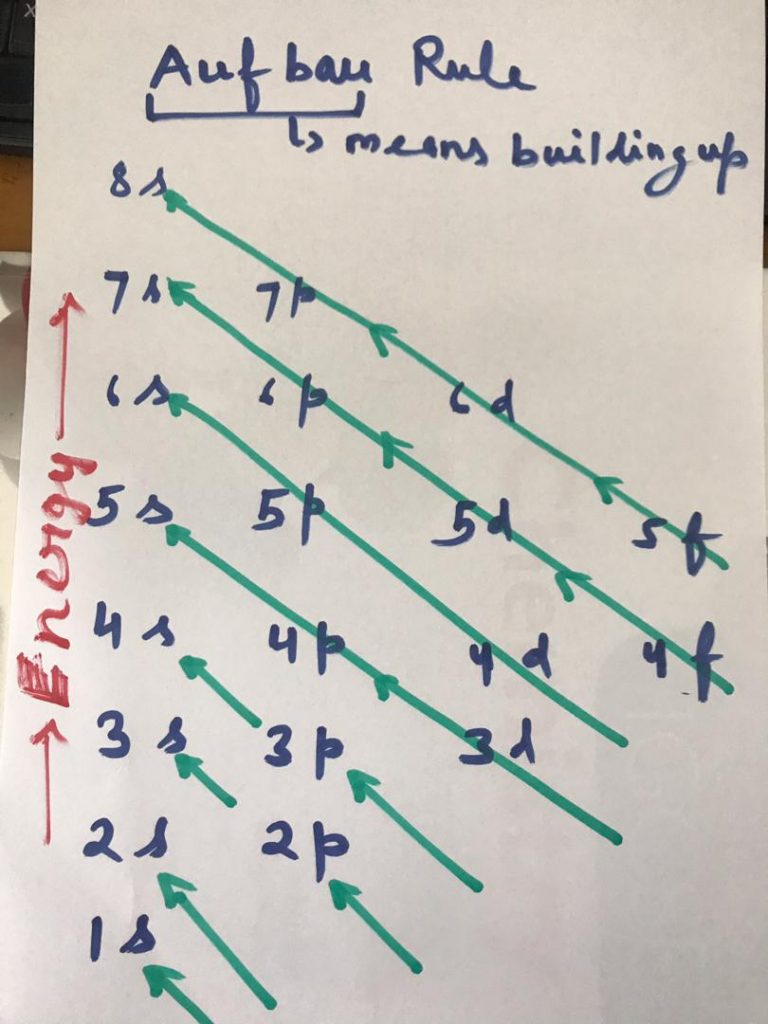
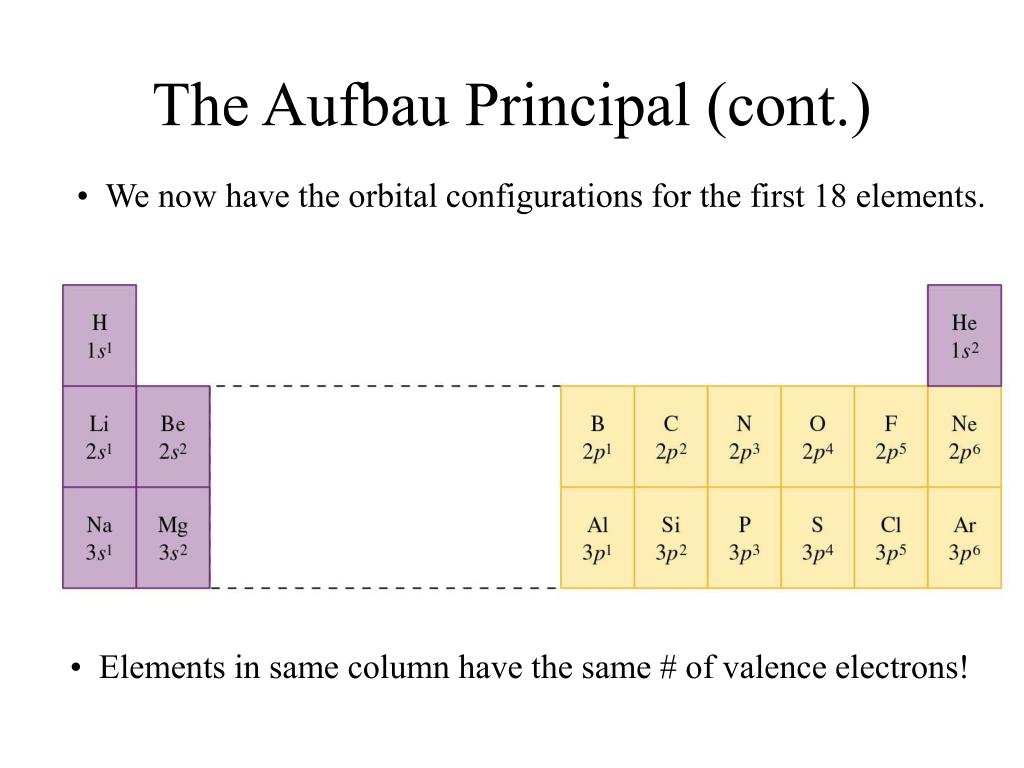
The term “Aufbau” has German roots and can be roughly translated as “construct” or “build-up.” The graphic below depicts the order in which atomic orbitals are filled. We can state the Aufbau principle as the available atomic orbitals with the lowest energy levels occupied first, followed by those with higher energy levels. It states that electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in the sequence of increasing orbital energy levels.

In general, the Aufbau principle governs how electrons are filled in an atom’s atomic orbitals in its ground state. Rules For Filling Electrons In Orbitals: Aufbau Principle Before proceeding, it is critical to understand that each orbital might be occupied by two electrons with opposing spins (which will be further discussed later). The Hund’s Rule, and the Pauli-Exclusion Principle are a collection of generic rules used to determine the electron configuration of an atomic species. The spin angular momentum associated with electron spin is distinct from the orbital angular momentum associated with electrons traveling around the nucleus.Īlso Read: Aufbau Principles in brief Electron Filling Rules Spin, like charge and rest mass, is a fundamental, unchanging feature of the electron. This angular momentum’s magnitude value is fixed. The quantum property of electrons is electron spin. Electrons are supplied in such a way that a high constant configuration is achieved. An atom is made up of subatomic particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons, with only the number of electrons being taken into account for electronic arrangement. It is the method or distribution of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. Chemists can anticipate an atom’s attributes, such as stability, boiling temperature, and conductivity, using the electron configuration and physical principles. The electron configuration of an atom is the orbital description of the electron locations in a typical atom. Overview of Aufbau PrincipleĮlectrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons, weighing over 1,800 times less than either. This principle is primarily concerned with the filling of electrons in an orbital during the composition of an electronic configuration. Unlike many other chemistry concepts, Aufbau is a German word that means “building up.” It is not the name of a scientist.

Noble gasses do not easily combine with other molecules since these orbital configurations are significant features. Furthermore, the most stable electron configuration possesses a complete energy state. Once an atom occupies all of its orbitals, it becomes the most stable and consequently unreactive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
